Arthritis Guide: Types, Diet, Symptoms & Management Tips
Types of Arthritis:
- Osteoarthritis:
- This is the most common
form of arthritis.
- It occurs when the
protective cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones wears down over
time.
- Common symptoms include
joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, often affecting the knees, hips, and
hands.
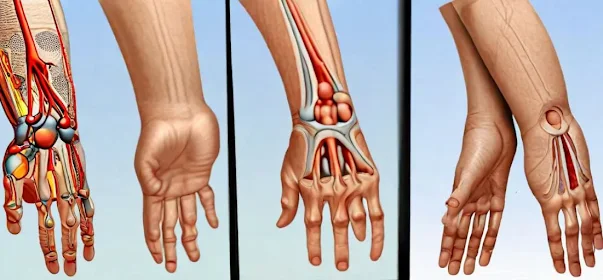
- Rheumatoid Arthritis:
- This is an autoimmune
disorder that occurs when the body's immune system attacks the lining of
the membranes that surround the joints.
- It can cause joint pain,
swelling, and can eventually result in joint deformity.
- It often affects the hands,
feet, and wrists.
Symptoms:
- Joint pain and tenderness
- Stiffness, particularly in
the morning or after resting
- Swelling and redness around
the joints
- Decreased range of motion
- In some types, symptoms can
include fatigue, fever, and loss of appetite
Causes:
- Genetics:- Family history can play a
role in the development of arthritis.
- Age:- The risk of many types of
arthritis, including osteoarthritis, increases with age.
- Gender:- Women are more likely than
men to develop rheumatoid arthritis, while men are more likely to develop
gout.
- Previous joint injury:- Injured joints are more
likely to develop arthritis.
- Obesity:- Excess weight puts stress
on joints, especially the knees, hips, and spine.
Diagnosis:
- Physical Examination:- Doctors will check for
joint swelling, redness, and warmth, and assess range of motion.
- Imaging Tests:- X-rays, MRI, and
ultrasound can help in diagnosing the extent of joint damage.
- Laboratory Tests:- Blood tests can identify
markers of inflammation and antibodies associated with certain types of
arthritis.
Treatment:
Medications:
- Pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen, ibuprofen)
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
- Biologic response modifiers
- Corticosteroids
Physical Therapy:
- Helps improve range of motion and strengthen the muscles around the joints.
Lifestyle Changes:
- Regular exercise
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Applying heat or cold to reduce pain
- Assistive devices for daily activities
Surgery:
In severe cases, procedures such as joint repair, joint replacement, or joint fusion may be necessary.
Managing arthritis typically involves a combination of treatments tailored to the individual's specific condition and needs. Regular medical check-ups and a proactive approach to treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Food and fruits that increase Arthritis
Certain foods and fruits can potentially exacerbate arthritis symptoms due to their inflammatory properties. It's important to note that individual reactions can vary, and some people might be more sensitive to certain foods than others. Here are some common foods and fruits that might increase inflammation and worsen arthritis symptoms:
Foods to Avoid:
- Sugary Foods and Beverages:
- High-sugar foods, including
candies, sodas, and desserts, can trigger the release of inflammatory
messengers called cytokines.
- Excessive sugar intake can also lead to weight gain, which puts additional stress on the joints.
- Refined Carbohydrates:
- White bread, white rice,
and pastries can increase inflammation and exacerbate arthritis symptoms.
- These foods have a high
glycemic index, which can spike blood sugar levels.
- Fried and Processed Foods:
- Foods high in unhealthy fats
and oils, such as fried foods, fast food, and processed snacks, can
promote inflammation.
- These foods often contain
trans fats, which are particularly harmful.
- Red Meat and Processed Meats:
- Red meats (beef, lamb,
pork) and processed meats (hot dogs, sausages) can contain high levels of
saturated fats and advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which can
increase inflammation.
- Dairy Products:
- Some people with arthritis
may find that dairy products, such as milk, cheese, and butter, can
increase joint pain due to the type of protein they contain.
- This varies by individual,
so it's important to monitor how your body reacts to dairy.
- Alcohol:
- Excessive alcohol
consumption can contribute to inflammation and negatively affect joint
health.
- It can also interact with
medications commonly prescribed for arthritis.
Fruits to Limit:
While
fruits are generally healthy, certain fruits might need to be consumed in
moderation by people with arthritis due to their potential inflammatory
properties or high sugar content.
- Citrus Fruits:
- Oranges, grapefruits,
lemons, and limes are rich in vitamin C, but some individuals might
experience an increase in arthritis symptoms after consuming them.
- This reaction varies, so
it’s important to monitor personal tolerance.
- Nightshade Vegetables:
- Tomatoes, along with other
nightshades like potatoes, eggplants, and peppers, contain solanine,
which some people believe can exacerbate arthritis pain. Scientific
evidence is mixed, but some individuals report improvement when avoiding
these.
- Fruits High in Fructose:
- High-fructose fruits, such
as apples, pears, and watermelon, can sometimes contribute to
inflammation in sensitive individuals.
- Moderation is key, as these
fruits also offer important nutrients.
Tips for Managing Diet with Arthritis:
- Focus on Anti-Inflammatory
Foods:- Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (like fatty fish),
antioxidants (like berries and leafy greens), and whole grains.
- Stay Hydrated:- Drinking plenty of water
can help maintain joint lubrication and overall health.
- Monitor Personal Triggers:- Keep a food diary to
identify which foods might be worsening your symptoms.
- Consult a Dietitian:- A registered dietitian can
help create a personalized eating plan that supports joint health and
overall well-being.
Adjusting
your diet can be an effective way to manage arthritis symptoms and improve your
quality of life.
Starting symptoms of Arthritis
- Joint Pain:
- Pain in the joints, which
may be constant or intermittent.
- Often worsens with movement
and improves with rest.
- Stiffness:
- Stiffness, especially in
the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Morning stiffness that
lasts longer than 30 minutes can be a sign of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Swelling:
- Swelling in one or more
joints, which may be accompanied by warmth and redness.
- Reduced Range of Motion:
- Difficulty moving the
joints as freely as before.
- A feeling of the joint
being "locked" or "stuck."
- Fatigue:
- Feeling unusually tired or
experiencing a general sense of malaise.
- Common in inflammatory types
of arthritis like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Joint Redness and Warmth:
- Redness and warmth around
the affected joints, indicating inflammation.
- Tenderness:
- Joints may feel tender to
the touch or when pressure is applied.
- Mild Fever:
- Low-grade fever can accompany
inflammatory types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
- Numbness or Tingling:
- Sensation of numbness or
tingling, particularly in the fingers or toes.
- Can occur due to nerve
compression associated with joint swelling.
Specific Early Symptoms Based on Arthritis Type:
- Osteoarthritis:
- Pain and stiffness in
weight-bearing joints (knees, hips).
- Crepitus (a grating
sensation) in the joint during movement.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis:
- Symmetrical joint pain
(affecting the same joints on both sides of the body).
- Fatigue, fever, and general
malaise.
- Development of small lumps
under the skin (rheumatoid nodules).
- Psoriatic Arthritis:
- Joint pain and swelling
accompanied by skin symptoms like psoriasis (red, scaly patches).
- Changes in the nails, such
as pitting or separation from the nail bed.
- Gout:
- Sudden, severe attacks of
pain, often starting in the big toe.
- Intense joint pain,
redness, and swelling.
If you
experience any of these symptoms, it's important to consult a healthcare
professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Early
diagnosis and intervention can help manage symptoms and prevent further joint
damage.
Immediate
first aid for Arthritis person
Immediate First Aid for Arthritis:
- Rest:
- Encourage the person to
rest the affected joint. Avoiding excessive movement can help reduce pain
and inflammation.
- Ice Therapy:
- Apply an ice pack or a cold
compress to the affected joint for 15-20 minutes. This can help reduce
swelling and numb the area to decrease pain.
- Be sure to wrap the ice
pack in a cloth to prevent direct contact with the skin, which can cause
frostbite.
- Compression:
- Use an elastic bandage or a
compression wrap to provide support to the affected joint. This can help
control swelling.
- Ensure the bandage is snug
but not too tight, as excessive pressure can restrict blood flow.
- Elevation:
- Elevate the affected limb
above the level of the heart to reduce swelling. This can be done by
propping the limb up on pillows.
- Heat Therapy:
- For some individuals,
applying heat can be more effective than ice, especially if the pain is
related to muscle stiffness or chronic arthritis.
- Use a warm towel, heating
pad, or take a warm bath for 15-20 minutes. Ensure the heat is not too
intense to avoid burns.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief:
- Nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help
reduce pain and inflammation.
- Acetaminophen can also be
used for pain relief, but it does not reduce inflammation.
- Always follow the dosage instructions
and consider any personal allergies or medical conditions.
- Topical Pain Relievers:
- Apply creams or gels
containing menthol, capsaicin, or salicylates to the affected joint.
These can provide temporary pain relief by numbing the area or creating a
warming sensation.
- Gentle Movement:
- After initial rest, gentle
range-of-motion exercises can help maintain joint flexibility. Avoid
strenuous activity and focus on gentle stretches.
- Hydration:
- Ensure the person stays
well-hydrated, as dehydration can sometimes worsen arthritis symptoms.
- Calm Environment:
- Provide a calm and
comfortable environment to reduce stress, which can exacerbate arthritis
symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
- Severe Pain:- If the pain is severe and
not relieved by over-the-counter medications.
- Sudden Swelling:- If there is sudden and
significant swelling in the joint.
- Fever:- If the person develops a
fever along with joint pain, it may indicate an infection.
- Deformity:- If there is a noticeable
deformity in the joint.
- Inability to Move the Joint:- If the person is unable to
move the joint or bear weight on it.
Thank you for visiting and reading this blog,
Mukhtar (India)




.jpg)








No comments:
Post a Comment